The compliance-only mentality is outdated.
Let’s be honest—when most healthcare organizations think about HIPAA compliant email, it’s usually in the context of avoiding fines or satisfying checklists. And while yes, compliance is critical, viewing it only through the lens of risk management is a missed opportunity.
In reality, HIPAA compliant email, when implemented properly, is one of the most powerful tools for patient and customer engagement. Why? Because it unlocks the ability to leverage protected health information (PHI) safely, enabling personalized, timely, and high-impact email communication that drives better engagement, satisfaction, and outcomes.
What Makes Email Truly HIPAA Compliant?
As a reminder, HIPAA compliant email requires that protected health information (PHI) is safeguarded both in transit and at rest. That means your email provider must:
- Use encryption at all times
- Be stored and transmitted in a secure manner
- Provide a Business Associate Agreement
Regular email services just don’t cut it. In fact, most consumer or marketing email platforms like Sendgrid or Constant Contact, while great at sending email, are not HIPAA compliant or have limitations when it comes to using PHI in your messages. Even when bolted-on encryption solutions are used, they often lack the flexibility, scalability, and automation needed for safe and effective healthcare email engagement.
LuxSci goes beyond the basics with policy-based encryption, secure TLS, PKI encryption and escrow/secure portal options. LuxSci’s SecureLine™ encryption technology dynamically selects the appropriate encryption method based on recipient capabilities and messaging context and can be configured to enforce secure delivery automatically according to organizational policies. LuxSci also provides the ability to enforce advanced multi-factor authentication. Every message is tracked with full audit trails—no guesswork, no loose ends.
The Real Opportunity – Secure, Personalized Email with PHI
Using PHI to Drive Personalized Messaging
Imagine sending a personalized reminder to a diabetic patient about an upcoming check-up. Or reaching out to new mothers with postnatal care resources tailored to their needs. Or sending automated email workflows to all your members to accelerate and increase new plan enrollments. Or email customer and prospects about a new product upgrade or new service offering. The list goes on. That’s the power of PHI-personalized email—when done securely.
Targeted Segmentation with Sensitive Data
With HIPAA compliant email solutions like LuxSci, you can segment your audience based on real health data with high levels of precision, such as chronic conditions, appointment history, insurance status, health risks, and more, without compromising patient trust or security.
Breaking the One-Size-Fits-All Approach in Healthcare Email
Generic email blasts are over. Modern patients expect personalization. With LuxSci, you can deliver highly targeted, highly secure emails with encrypted content, while staying HIPAA compliant.
Real Business Results from Secure Email
Here’s how secure, personalized email can drive improved results across a range of healthcare communications, including:
- Increased Patient Appointments and Follow-ups – Sending encrypted, personalized appointment reminders and follow-up notices can reduce no-shows and boost overall appointment volume.
- Boosting Preventative Care with Outreach Campaigns – Preventative campaigns (think flu shots or cancer screenings) sent securely to the right segments can lead to higher response rates, better health outcomes, and a lower cost of care.
- Improving Health Plan Enrollments – Targeted email outreach during open enrollment, tailored by eligibility or plan type, and powered by automated workflows leads to higher enrollments and lower call center costs.
- Driving Awareness and Sales of New Services or Products – Have a product upgrade offer, new wellness program or telehealth service? Send secure, PHI-informed HIPAA compliant email to the right audience for increased sales and faster adoption.
- Optimize Explanation of Benefits Notices – Replace snail mail with email that’s fast, reliable and trackable, ensuring customers are informed and compliance is met.
The Healthcare Marketer’s Secret Weapon: Using PHI Responsibly
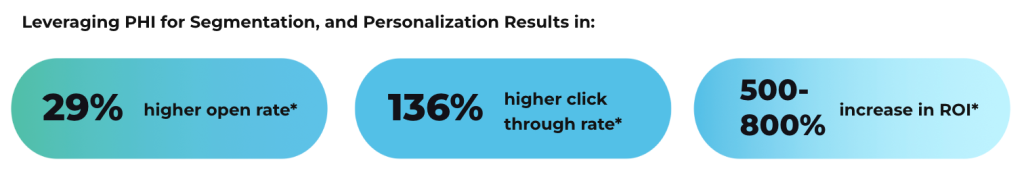
In a world moving away from third-party cookies, first-party data is more valuable than ever, and PHI is the most powerful form of it in healthcare. With secure HIPAA compliant email, PHI doesn’t have to be locked away. Marketers can safely use it to understand patient needs and send relevant, timely messages. PHI-driven segmentation lets you build hyper-targeted campaigns that speak to relevant conditions, unique needs and timely topics, increasing open rates, clicks throughs, and campaign conversions.
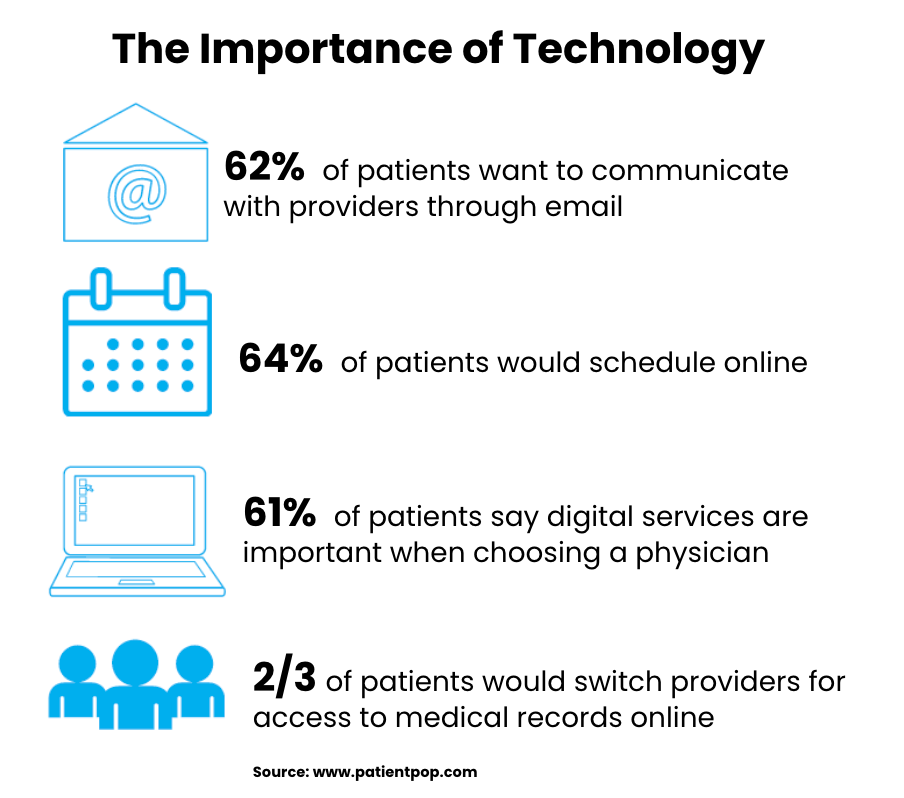
Meeting the Personalization Demands of Today’s Patients and Customers
HIPAA-compliant email is no longer just about checking a box. It’s about unlocking the full potential of your patient and customer data to drive better engagement, healthier outcomes, and measurable business results.
In closing, below are some final thoughts on how secure, HIPAA compliant email delivers long-term value for your organization and better connections with your patients and customers, including:
-
- Future-Proofing Healthcare Engagement – Patients expect Amazon-level personalization. HIPAA-compliant tools let you meet those expectations securely.
-
- Adapting to Data Privacy Regulations Beyond HIPAA – From GDPR to state-level privacy laws, secure communication is no longer optional, it’s foundational.
-
- Building Trust Through Secure Communication – Each secure, personalized message sent is a trust-building moment with your patients and customers.
Why LuxSci? The Infrastructure Behind the Performance
With LuxSci’s secure email infrastructure and email marketing solutions, healthcare organizations can confidently personalize communication, reach patients more effectively, and fuel growth with PHI-safe segmentation, messaging, and email automation.
LuxSci takes data security and email performance to the next level by offering dedicated cloud infrastructure for each customer, which means your email campaigns aren’t slowed down by other vendors on shared cloud services and your attack footprint is much smaller. In short, you get higher delivery rates and throughput with proven HIPAA compliance and data security.
The future of healthcare engagement is personal, secure, and performance-driven—and it starts with HIPAA compliant email done right.
Reach out today with any questions or to learn more about LuxSci.
FAQs
1. Is HIPAA-compliant email necessary for marketing communications?
Yes—if your emails include or are based on PHI (like appointment reminders, condition-based messaging, or insurance info), you need HIPAA-compliant email and recipient consent to avoid legal risk and preserve patient trust.
2. Can PHI be used in marketing emails under HIPAA?
Yes, with proper consent and secure, HIPAA compliant infrastructure like LuxSci’s, PHI can be safely used in emails for personalized, segmented campaigns.
3. How does LuxSci ensure high email deliverability for healthcare messages?
LuxSci uses dedicated cloud servers for each customer, active email reputation monitoring, and best-practice configurations to ensure high deliverability rates for sensitive emails.
4. Is LuxSci only for marketing teams?
No—LuxSci supports marketing, clinical, operations, and IT teams by enabling secure, compliant email communication across the entire organization.
5. What types of PHI can I use to segment campaigns using LuxSci?
You can segment based on chronic conditions, visit history, insurance status, provider details, age, gender, location, and more—all while staying fully compliant.