Email deliverability refers to the ability of emails to reach recipients’ inboxes successfully without being filtered into spam folders or blocked entirely by email service providers. This metric encompasses the entire journey an email takes from sender to recipient, including authentication protocols, sender reputation, content quality, and recipient engagement patterns. For healthcare organizations managing patient communications, provider networks, and supplier relationships, understanding email deliverability becomes particularly important given the sensitive nature of healthcare data and the need for reliable communication channels. Healthcare providers, payers, and suppliers who master email deliverability can maintain better patient relationships, reduce administrative costs, and avoid compliance issues that arise from failed communications.
How Email Service Providers Evaluate Messages
Email service providers use algorithms to evaluate incoming messages and determine their appropriate destination within recipient email systems. These systems analyze multiple factors simultaneously, including sender authentication records, message content, sending patterns, and recipient behavior. The filtering process occurs in real-time, with providers like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo applying machine learning models trained on billions of email interactions to identify potential spam or malicious content.
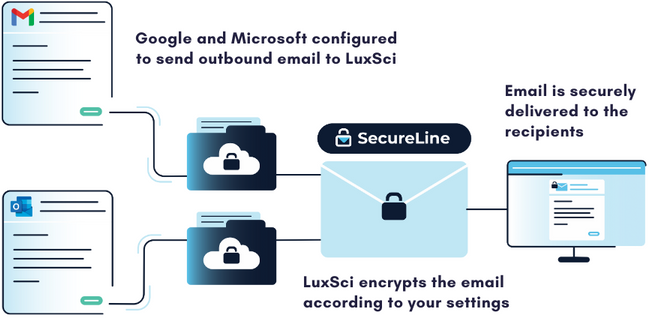
Authentication plays a large role in this filtering process through verification of sender identity. Providers verify sender identity through SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) records. Healthcare organizations without properly configured authentication often find their appointment reminders, lab results, or billing communications relegated to spam folders, disrupting patient care workflows and administrative processes.
Content analysis represents another layer of filtering, where providers examine subject lines, message body text, and embedded links for spam indicators. Healthcare communications containing medical terminology, prescription information, or insurance details may trigger false positives if not properly formatted or if sent from domains with poor reputation scores. The complexity of these filtering systems means that even legitimate healthcare communications can face delivery challenges without proper optimization.
Recipient engagement metrics influence future email deliverability for healthcare organizations, as providers track open rates, click-through rates, and spam complaint rates. When patients consistently ignore or delete emails from healthcare organizations, providers may begin filtering future messages more aggressively. This creates a feedback loop where poor engagement leads to worse delivery rates, making it increasingly difficult to reach patients with important medical information.
Sender Reputation and Healthcare Communications
Sender reputation functions as a digital credit score for email domains and IP addresses, influencing whether healthcare organizations can reliably reach patients, providers, and business partners. Email service providers maintain reputation databases that track sending behavior, bounce rates, spam complaints, and recipient engagement over time. A single domain or IP address with poor reputation can affect email deliverability across an entire healthcare network, creating widespread communication problems.
Healthcare organizations face unique reputation challenges due to the nature of their communications and patient populations. Patient appointment reminders sent to outdated email addresses generate high bounce rates, while automated billing notifications may receive spam complaints from recipients who forgot they subscribed to such communications. These factors can gradually erode sender reputation, making it increasingly difficult to reach patients with time-sensitive medical information or coordinate care between providers.
The healthcare industry’s regulatory environment adds complexity to reputation management, as organizations must balance effective communication with privacy requirements. HIPAA compliance considerations may limit how organizations can personalize emails or track recipient behavior, potentially affecting engagement metrics that influence sender reputation. Healthcare organizations tackle these constraints while maintaining the communication effectiveness needed for patient care and business operations.
Reputation recovery in healthcare settings requires sustained effort and careful monitoring of multiple factors. Organizations must implement proper list hygiene practices, authenticate their domains correctly, and monitor feedback loops from major email providers. The process can take weeks or months, during which patient communications may continue experiencing delivery issues that could impact care coordination and administrative efficiency. Proactive reputation management helps prevent these problems before they affect patient care.
Authentication Protocols for Healthcare Email Security
Modern email deliverability depends heavily on proper implementation of authentication protocols that verify sender identity and prevent email spoofing attempts. SPF records specify which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of a domain, while DKIM adds cryptographic signatures to verify message integrity. DMARC ties these protocols together by instructing receiving servers how to handle emails that fail authentication checks, providing policy guidance for email providers.
Healthcare organizations must configure these protocols carefully to avoid authentication failures that could block legitimate patient communications. A misconfigured SPF record might prevent appointment confirmation emails from reaching patients, while improper DKIM setup could cause lab result notifications to be filtered as spam. These authentication failures can have serious implications for patient care, particularly when dealing with urgent medical communications or time-sensitive treatment instructions.
The implementation process requires coordination between IT teams, email service providers, and third-party healthcare applications that send email on behalf of the organization. Many healthcare systems use multiple platforms for patient communications, billing, and administrative functions, each requiring proper authentication configuration to maintain good email deliverability across all communication channels. This complexity makes authentication management an important component of healthcare IT operations.
Regular monitoring and maintenance of authentication protocols helps ensure continued email deliverability for healthcare organizations. DNS records can change unexpectedly, third-party applications may modify their sending practices, and email providers periodically update their authentication requirements. Healthcare organizations benefit from establishing procedures for ongoing authentication monitoring and having technical expertise available to address configuration issues quickly when they arise.
Content Quality and Compliance Considerations
Email content quality directly affects deliverability, with providers using advanced algorithms to evaluate message structure, language patterns, and formatting for spam indicators. Healthcare organizations must balance informative content with delivery requirements, ensuring that medical communications reach their intended recipients without triggering spam filters. This balance is challenging when dealing with complex medical terminology, prescription information, or insurance-related content that may resemble spam to automated filtering systems.
HIPAA compliance adds another layer of complexity to healthcare email content, as organizations must protect patient information while maintaining effective communication channels. Emails containing protected health information require additional security measures and careful content formatting to avoid both compliance violations and deliverability issues. The challenge is in creating compliant, informative communications that also pass through increasingly sophisticated spam filters without compromising patient privacy or care quality.
Subject line optimization also plays a role in healthcare email deliverability, as providers analyze these elements for spam indicators and patient engagement patterns. Generic subject lines like “Appointment Reminder” or “Lab Results Available” may perform differently across various email providers, requiring healthcare organizations to test and optimize their messaging strategies while maintaining compliance with healthcare communication regulations. Personalization can improve engagement but must be balanced with privacy requirements and spam filter sensitivities.
Message formatting and design elements influence both deliverability and patient engagement with healthcare communications. HTML emails with excessive images, complex layouts, or suspicious formatting may trigger spam filters, while plain text messages may not engage recipients effectively. Healthcare organizations must find the right balance between visual appeal and delivery reliability, often requiring testing across multiple email clients and providers to ensure consistent performance.
List Management and Patient Engagement Strategies
Effective list management forms the foundation of sustainable email deliverability for healthcare organizations managing communications with patients, providers, and suppliers. Clean, engaged recipient lists generate better delivery rates and help maintain positive sender reputation over time. Healthcare organizations must implement systematic approaches to list hygiene, including regular removal of bounced email addresses, management of unsubscribe requests, and monitoring of engagement patterns across different communication types.
Patient engagement patterns in healthcare differ significantly from typical marketing communications, as medical emails often contain information that recipients need rather than want. Appointment reminders, lab results, and billing notifications serve functional purposes that may not generate traditional engagement metrics like high open rates or click-through rates. Understanding these patterns helps healthcare organizations optimize their sending strategies without compromising the informational value of their communications or patient care quality.
Segmentation strategies in healthcare email deliverability focus on communication types and recipient preferences rather than demographic targeting approaches. Patients may engage differently with preventive care reminders compared to urgent test results, requiring sending approaches that consider both deliverability factors and patient communication preferences. This segmentation helps maintain good sender reputation while ensuring that different types of healthcare communications reach their intended recipients effectively.
Data quality management includes verification of patient contact information, preference management, and communication history tracking. Healthcare organizations benefit from implementing processes to capture updated email addresses during patient visits, verify contact information through multiple channels, and maintain records of communication preferences that respect patient choices while supporting care coordination needs. These practices improve both deliverability and patient satisfaction with healthcare communications.
Maintaining Email Deliverability Performance
Monitoring of email deliverability metrics provides healthcare organizations with the data needed to identify and address communication issues before they impact patient care or administrative operations. Key metrics include delivery rates, bounce rates, spam complaint rates, and inbox placement percentages across different email providers. These metrics help organizations understand how their communications perform across various platforms and identify potential problems with specific communication types or recipient segments.
Healthcare organizations should establish monitoring systems that track deliverability performance across different communication channels, including patient portal notifications, appointment reminders, billing communications, and provider-to-provider messages. This approach helps identify patterns that might indicate authentication issues, content problems, or reputation concerns that could affect the organization’s ability to communicate effectively with patients and business partners. Regular analysis of these patterns enables proactive problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Deliverability testing and optimization require ongoing attention to changing email provider policies, spam filter updates, and evolving patient communication preferences. Healthcare organizations benefit from implementing A/B testing for subject lines, send times, and content formats while maintaining compliance with healthcare regulations. Testing should include evaluation of deliverability performance across different email clients, devices, and providers to ensure consistent communication effectiveness.
Regular deliverability audits should include testing of authentication protocols, review of sender reputation scores, analysis of content performance, and evaluation of list management practices. These audits help healthcare organizations maintain optimal email deliverability while ensuring that their communication strategies remain aligned with both technical requirements and healthcare industry best practices for patient communication and data protection. Documentation of audit results and remediation activities shows commitment to maintaining reliable patient communications and regulatory compliance.