The best HIPAA compliant email contains strong security features with ease of use and reasonable pricing. Top options include properly configured email accounts with Business Associate Agreements in place. Look at HIPAA compliant email platforms that offer encryption, access controls, audit logging, and secure mobile access while fitting practice size, budget, and capabilities. Healthcare organizations selecting the best HIPAA compliant email solutions need platforms that integrate seamlessly with existing workflows while providing robust protection for patient communications across all devices and locations.
HIPAA Compliant Email Features
Healthcare professionals require email systems with particular security capabilities to protect client communications. Any HIPAA compliant email must include automatic encryption that works without requiring clients to create accounts or remember passwords. You need detailed access logs that document when messages were sent, received, and viewed. Message recall capabilities help address accidental disclosures before they become compliance issues. Calendar integration supports secure appointment scheduling and reminders. Mobile access controls ensure therapists can communicate safely from smartphones and tablets during off-hours or between office locations. Document sharing features allow secure exchange of intake forms and treatment plans. These capabilities help therapists maintain compliant communications while managing their practice efficiently.
Archive management capabilities preserve historical communications for required retention periods while maintaining searchability and security protections. Healthcare providers need email systems that can retrieve past communications quickly during audits or patient requests without compromising protection standards. Automated retention policies delete expired messages according to regulatory requirements, reducing data exposure risks over time. Version control tracks message modifications and forwarding activities, creating complete audit trails that demonstrate proper information handling. The best HIPAA compliant email platforms balance preservation requirements with operational efficiency, ensuring that providers can access necessary historical communications without maintaining unnecessary data repositories.
Popular HIPAA Compliant Email Platforms
Several email providers offer solutions well-suited to mental health professionals. Mainstream platforms provide affordable options when properly configured with appropriate security settings and covered by Business Associate Agreements. Smaller therapy practices prefer familiar platforms for their integration with other practice tools. Healthcare organizations benefit from email solutions that work with existing technology infrastructure rather than requiring complete system replacements.
Platform selection depends on practice size, technical expertise, and specific workflow requirements that vary across medical specialties. Primary care practices need different features compared to specialty clinics or multi-location healthcare systems. Solo practitioners value simplicity and minimal maintenance requirements, while larger organizations need centralized administration and consistent policy enforcement. Integration capabilities determine how well email systems connect with electronic health records, practice management software, and billing systems that support daily operations.
Security Considerations for Healthcare Communications
Secure healthcare communications require thoughtful security approaches due to their sensitive nature. HIPAA compliant email should include protections against phishing attacks that might target patient information. Data loss prevention tools identify and secure messages containing sensitive information even when users forget to enable encryption. Account recovery procedures must balance security with practicality for small practices. Multi-factor authentication prevents unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised.
Healthcare personnel handling substance use disorder information need email systems that comply with both HIPAA and 42 CFR Part 2 requirements. Solutions should accommodate supervision relationships where communications may need controlled sharing with supervisors. Mental health providers managing adolescent patients need systems that respect parental access rights while protecting minor privacy in accordance with state laws.
Threat detection capabilities monitor email systems for unusual access patterns, suspicious login attempts, or unauthorized data export activities that might indicate security breaches. Real-time alerting notifies administrators when potential security incidents occur, enabling rapid response before patient information is compromised. Automated threat response systems can temporarily lock accounts, require password resets, or restrict access when suspicious activities are detected. Healthcare organizations implementing the best HIPAA compliant email need layered security defenses that protect against both external attacks and internal policy violations.
Client Experience and Usability Factors
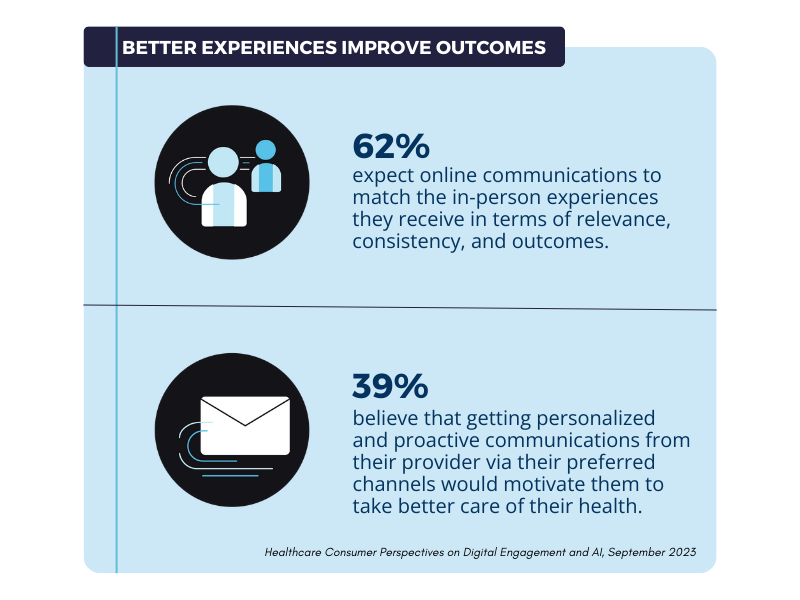
The best HIPAA compliant email solutions balance security with positive client experiences. Buyers should evaluate how encryption affects the client’s process for reading and responding to messages. Some solutions require clients to create accounts or install software, while others deliver protected messages that open with minimal friction. Mobile compatibility matters as many clients prefer communicating from smartphones. Branding options allow therapists to maintain professional appearance in all communications. Automated responses help set appropriate expectations about response timing and emergency protocols. Client-facing secure forms streamline intake processes while maintaining compliance.
Patient education materials help individuals understand how to use secure email systems effectively while protecting their own information. Clear instructions about recognizing legitimate healthcare emails prevent patients from falling victim to phishing attempts that impersonate medical providers. Guidance about password protection and account security empowers patients to participate actively in safeguarding their health information. Healthcare providers benefit from email platforms that include patient-facing documentation explaining security features and proper usage.
Communication preference tracking enables healthcare organizations to document which patients consent to email communications versus those preferring telephone or postal mail contact. Preference management systems ensure staff use appropriate communication channels for different patients based on documented choices. Alternative communication methods should remain available for patients who decline electronic communications or lack reliable email access, ensuring that digital communication options expand rather than limit healthcare accessibility.
HIPAA Compliant Email Implementation for Medical Practices
Implementing secure email requires planning tailored to medical practice workflows. Solo practitioners need solutions with straightforward setup and minimal maintenance. Group practices benefit from centralized administration that enforces consistent security policies across all providers. Practice management integration connects secure email with scheduling, billing, and documentation systems.
Transition planning helps migrate existing communications to new secure platforms without disrupting client relationships. Documentation templates ensure compliance with both HIPAA and professional ethical standards for electronic communications. Training materials must cover both operational procedures and appropriate clinical use cases. When implementing HIPAA compliant email, practice admins should create workflow procedures that incorporate secure communication into practice routines.
Change management strategies help staff adapt to new communication technologies without resistance that could undermine security measures. Phased implementation approaches allow practices to introduce secure email gradually, starting with internal communications before expanding to patient-facing uses. Pilot programs with limited user groups identify workflow issues before organization-wide deployment. Feedback collection during implementation phases reveals usability problems that might discourage adoption or encourage workarounds that compromise security.
Staff training programs need recurring sessions rather than one-time orientations, as communication security requires ongoing attention to evolving threats and changing regulations. Scenario-based training helps staff understand appropriate email usage through realistic examples of common situations they might handle. Role-specific training addresses different security responsibilities for physicians, nurses, administrative staff, and IT personnel. Assessment procedures verify that staff comprehend security protocols before granting access to patient communication systems.
Cost Considerations For Selecting Email Services
Healthcare providers must balance security requirements with budget realities when selecting HIPAA compliant email. Pricing models vary, with some services charging per user while others offer flat-rate plans better suited to solo practitioners. Fees may apply for features like secure forms, extra storage, or advanced security controls. Implementation costs include time spent on configuration, training, and client education about new communication methods. Some platforms offer discounted rates for professional association members or multi-year commitments. Buyers should calculate the total cost of ownership beyond monthly subscription fees, including support and compliance documentation. Affordable HIPAA compliant email options exist for practices of all sizes, but require thoughtful evaluation of both immediate pricing and long-term value.
Hidden costs emerge from email system complexity that requires specialized IT support or consultant assistance during setup and maintenance. Training expenses accumulate when staff turnover necessitates repeated onboarding for new employees unfamiliar with secure communication protocols. Compliance documentation costs include time spent maintaining audit trails, conducting security assessments, and preparing evidence for regulatory inspections. Healthcare organizations should budget for these indirect expenses when comparing email platform options.
Return on investment calculations should account for productivity improvements from efficient communication workflows, reduced compliance violation risks, and enhanced patient satisfaction with convenient digital access. Email systems that integrate with existing healthcare software reduce duplicate data entry and streamline administrative tasks, creating time savings that offset subscription costs. Improved patient engagement through convenient communication channels can increase appointment attendance, medication adherence, and referral rates that support practice growth.
Integrating Email with Broader Practice Security
HIPAA compliant email represents one component of broader practice security. Email solutions should complement electronic health record systems while maintaining appropriate boundaries between clinical documentation and communications. Device management policies ensure providers access email securely across computers, tablets, and smartphones. Backup procedures preserve communications while maintaining security protections. Incident response planning prepares organizations for addressing potential security issues or breaches. Reviews evaluate whether email practices continue to meet evolving compliance requirements. By integrating email security with broader practice safeguards, healthcare providers create communication systems that protect client information throughout its lifecycle.
Network security architecture determines how email systems connect with other healthcare applications and external networks while maintaining isolation from potential threats. Firewall configurations control which external systems can communicate with healthcare email servers, preventing unauthorized access attempts. Intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns that might indicate cyberattacks targeting patient communications. Segmented networks separate email systems from less secure applications, limiting potential damage if other systems are compromised.
Disaster recovery planning ensures that email communications can be restored quickly after system failures, natural disasters, or security incidents without losing patient information. Geographic redundancy stores email data in multiple locations, protecting against localized failures that could disrupt healthcare operations. Regular backup testing verifies that archived communications can be recovered successfully when needed. Recovery time objectives define acceptable downtime periods for email systems based on their importance to patient care activities