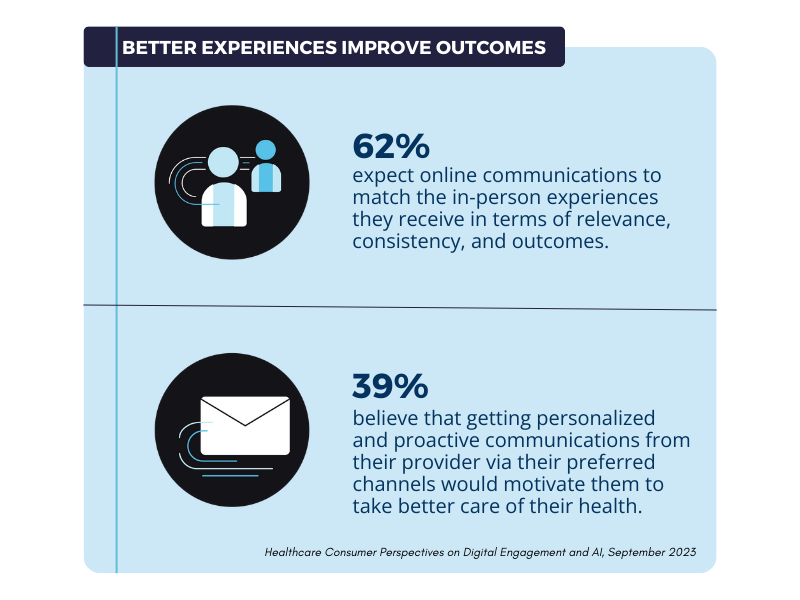
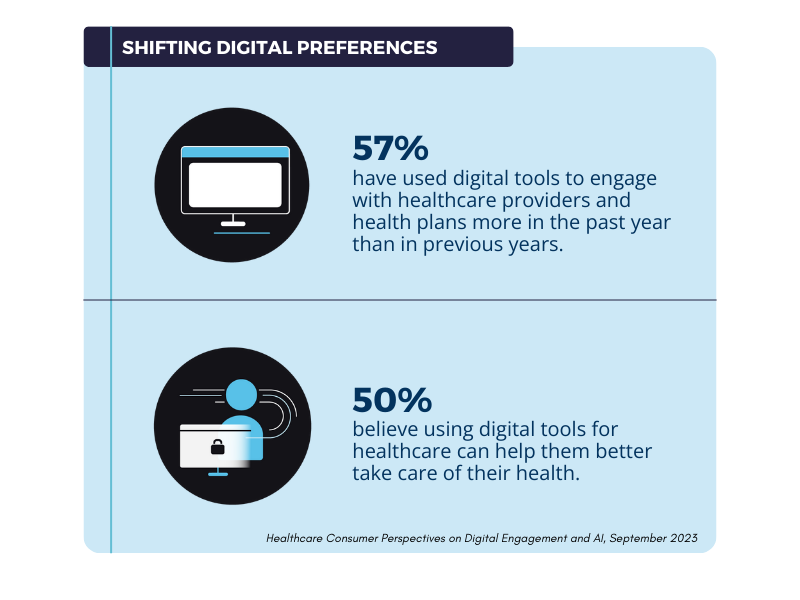
With email communication playing a critical role in the customer engagement strategies of virtually every organization, high email deliverability rates are vital to success across all industries. In the healthcare sector, however, the stakes can be far higher. An undelivered email isn’t merely an inconvenience or a lost sales opportunity; it could mean a missed appointment, a delay in a prescription refill, or a failure to get a patient critical healthcare information. Or worse, the email could end up in the hands of an unintended recipient, including bad actors and cybercriminals.
With this in mind, this post details why high email deliverability is essential for healthcare companies, as well as how your organization benefits from reliable and rapid email delivery.
Speed and Efficiency
The primary reason that high email deliverability is crucially important to healthcare organizations is to best guarantee essential communications that directly impact an individual’s healthcare journey reach them promptly. These transactional emails can include appointment reminders, prescription renewals, product order confirmations, test results, explanation of benefits notices, payment reminders, and invoices. Administrative notifications related to software or systems that a patient might use, such as a password reset for an online portal, also fall under the category of transactional emails.
When transactional emails are delayed or fail to reach people altogether, they can compromise a patient’s ability to access care, adhere to treatment plans, stay informed on key facets of their healthcare journey, and, ultimately, achieve optimal health outcomes.
When a patient fails to receive an expected email, such as a prescription confirmation, for example, it can leave them feeling confused and unsure of what to do next. For individuals who are sick, elderly, or managing chronic conditions, this can cause unnecessary stress, anxiety, and even compromise adherence to care plans.
In contrast, high email delivery rates create the opposite effect, helping patients get the communications and information they need. This increases their trust in your company and gives them a firmer sense of control over their healthcare journey.
Compliance with HIPAA Regulations
While the above point stresses the importance of reliable email delivery for the patient’s and customer’s benefit, healthcare companies also have a vested interest in ensuring communications reach the intended recipient for regulatory and patient privacy reasons.
To comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), emails that contain sensitive patient data, i.e., electronic protected health information (ePHI), must be securely delivered to the intended recipient. If, on the other hand, a communication containing ePHI fails to reach the intended recipient patient, that represents a failure in secure communications and a potential HIPAA violation for your organization.
After all, where did the patient’s data go? Was it delivered to the wrong person? Was it blocked by a spam filter and is left sitting unencrypted on a server somewhere?
If you can’t answer these questions, you could be exposed to a data breach, and it could result in a HIPAA violation, meaning your organization incurrs the associated consequences, including financial penalties and reputational damage. Conversely, deploying a fully HIPAA compliant email solution, such as LuxSci, supported by a dedicated infrastructure and designed for high email delivery enables your organization to include patient data in communications with confidence and ensure you messages land in the recipient’s inbox.
Greater Levels of Personalization and Engagement
Finally, high email deliverability rates are essential for healthcare organizations because they help drive greater levels of engagement with patients and customers. Higher email deliverability means better inbox placement, leading to more emails being opened, more links being clicked, and more conversions for your communications and campaigns.
In the case of healthcare retailers, for example, this equates to converting more prospects into customers and, consequently, maximizing the ROI of email marketing campaigns, in some cases with up to 80% better results.
While healthcare marketers, understandably, focus most of their efforts on crafting attention-grabbing headlines, personalizing the message content, and the email’s design elements, these factors are rendered irrelevant if the message fails to reach the recipient in the first place! When you take this into account, high email deliverability is a crucial component in optimizing the ROI of email communications and campaigns, and an all too often overlooked component at that.
Get Your Copy LuxSci’s Achieving High Email Deliverability Best Practices Paper
To learn more about the importance and value of high email deliverability for healthcare companies, download your copy of LuxSci’s latest Best Practices Paper: How to Achieve High Email Deliverability in Healthcare. You’ll discover:
- How to opitmize performance for the different types of healthcare emails.
- Powerful strategies for increasing your company’s email deliverability rates.
- How small increases in email deliverability can have considerable effects on your marketing ROI
Grab your copy of the report here, and learn how to enhance your email deliverability rates today.